Shopify Catalog Operations & Automation
Structured catalog, bulk updates, and reliable automation in Shopify
Overview
This case study shows end-to-end execution in a live Shopify store. It covers product setup, variant modeling, data enrichment, bulk updates with comma separated values files, inventory and price changes, metafields for attributes, faceted filters, and automated stock tagging. The goal is clean data and fast operations. It proves how taxonomy and metadata decisions drive storefront behavior, scalable updates, and hands-off merchandising.
Jump to Section
1. Catalog Setup and Enrichment
2. Automated Inventory Tagging and Merchandising Rules
3. Bulk Product CSV Build and Import
4. Bulk Variant Price Update via CSV Export and Re-Import
5. Bulk Inventory Update via CSV Export and Re-Import
6. Site Filters and Product Recommendations (Search and Discovery)
7. Conclusion
1. Catalog Setup and Enrichment
This section documents the foundation of the Shopify catalog. Products were first modeled and uploaded using a CSV file, then enriched directly in the admin with structured attributes, variant options, and standardized categories. Every detail—from product taxonomy to SEO metadata—was built to ensure data consistency, search visibility, and readiness for automation.
1a. Catalog Import File
Source file used to create products and variants with clean option sets, handles, SKUs, and categories.
1b. All Products List
Products created from the CSV are live, named consistently, categorized, and published to channels.
1c. Inventory View
Full inventory view confirming every variant has a unique SKU and on-hand quantity tracked.
1d. Product Admin Page
One product shown end-to-end with title, description, images, variant options, pricing, category, metafields, and search details.
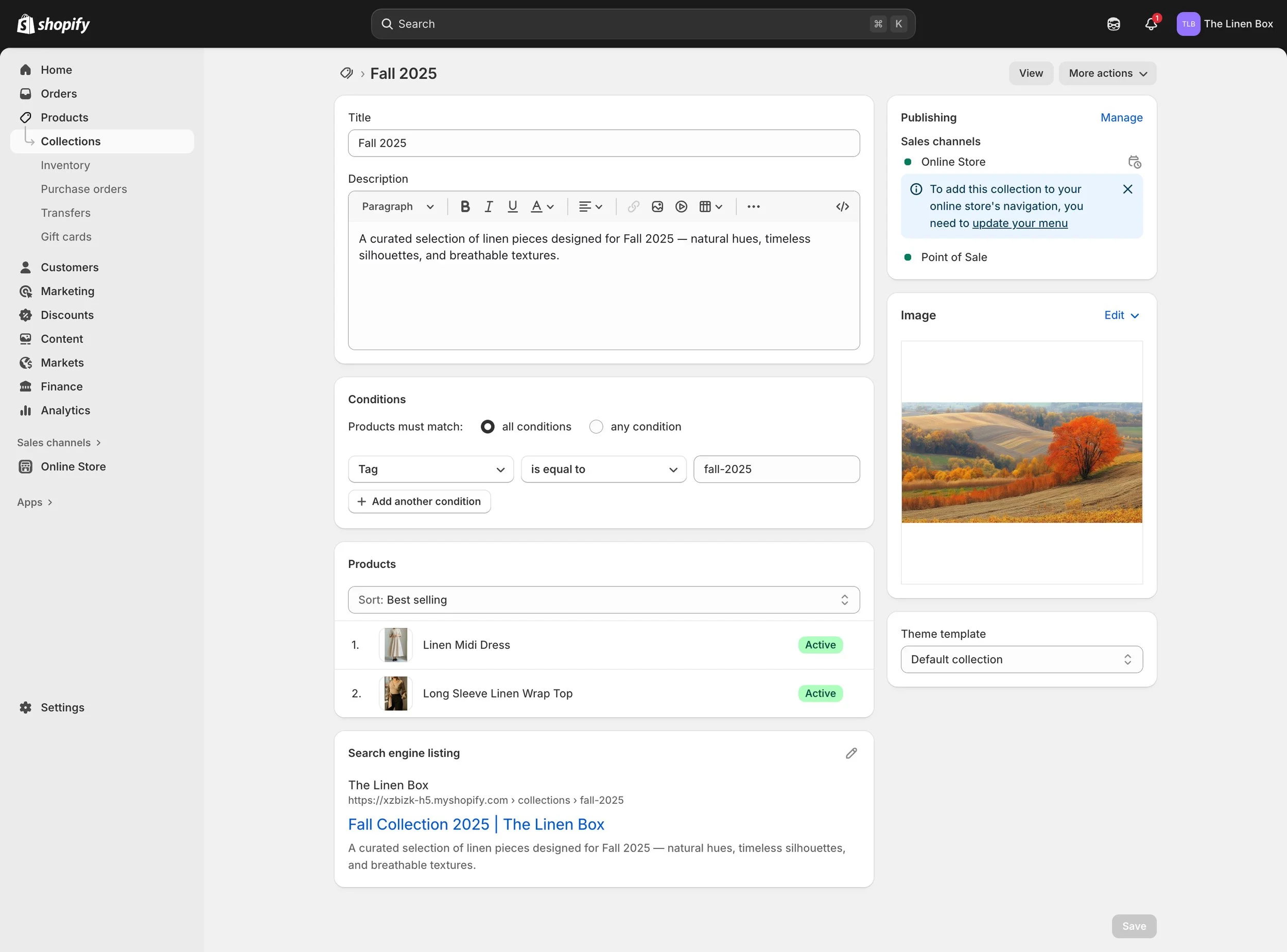
1e. Smart Collection Rules
Rule-based collection that pulls items by tag for hands-off grouping and clean URLs.
2. Automated Inventory Tagging and Merchandising Rules
To reduce manual catalog upkeep, I built automation flows that apply and clear inventory-status tags in real time. These workflows ensure products are always labeled accurately, surface low-stock items for action, and remove products from promotional collections once they sell out. This protects the customer experience and keeps merchandising decisions fast and data-driven.
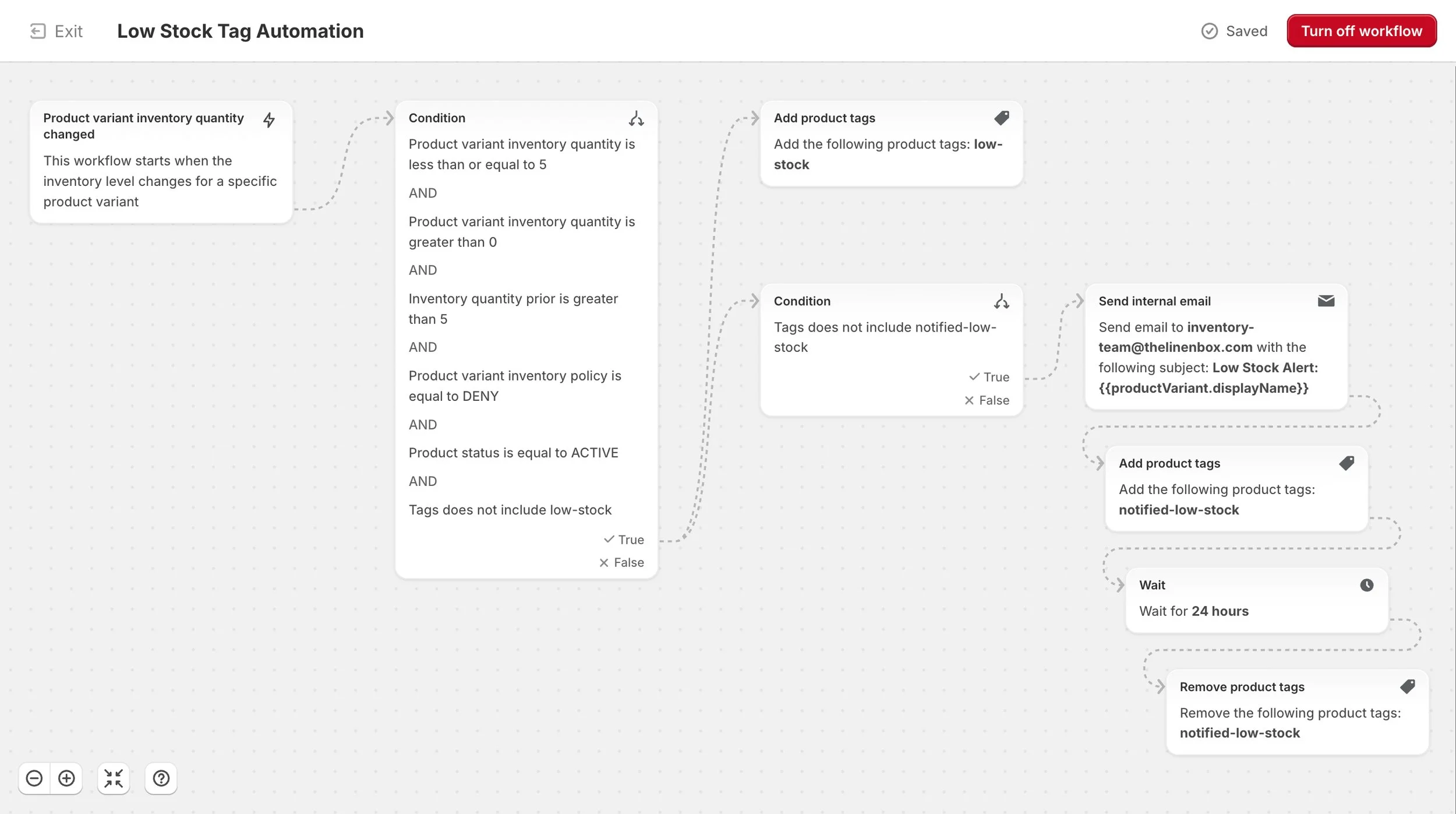
2a. Low-Stock Tag Automation
This automation monitors inventory for each variant and tags products as “low-stock” when quantity drops to five or fewer units. It also sends an internal alert and applies a temporary “notified-low-stock” tag that clears after 24 hours to prevent duplicate emails. This keeps catalog signals and internal workflows aligned without manual checks.
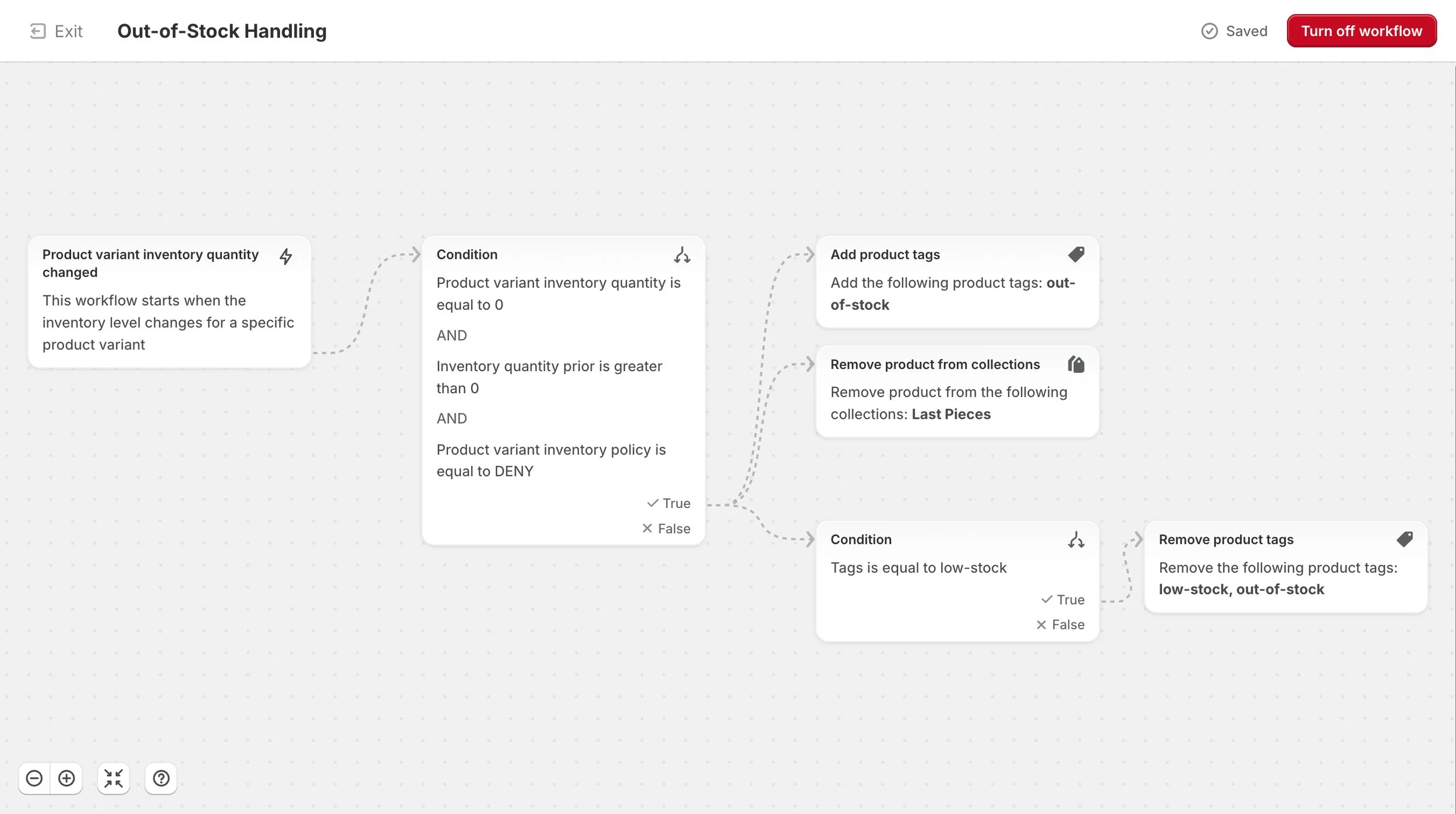
2b. Out-of-Stock Handling
When a variant reaches zero inventory, this workflow applies an “out-of-stock” tag, removes the item from the “Last Pieces” collection, and clears any “low-stock” tags. This ensures sold-out products are labeled immediately and hidden from last-chance shopping buckets as soon as they run out, protecting accuracy and customer transparency.
2c. Restock Tag Cleanup
When inventory rises above the low-stock threshold again, this flow automatically removes “low-stock” and “out-of-stock” tags and clears the product from the “Last Pieces” collection. This prevents incorrectly marked products from remaining flagged as limited, supporting clean merchandising and correct product availability signals site-wide.
3. Bulk Product CSV Build and Import
I built a new product (Oversized V-Neck T-Shirt) and all variants in a CSV using Shopify’s sample CSV import template, then imported it into Shopify, enriched the product with categories, tags, images, and SEO fields, verified variant data and inventory, and published it. The workflow shows clean data structure, accurate variant creation, and a polished storefront result — turning a spreadsheet build into a fully merchandised live product.
3a. Shopify Product CSV
Shopify-import formatted CSV defining product names, variant rows, SKUs, pricing tiers, and inventory fields, built for accurate bulk upload and scalable catalog updates.
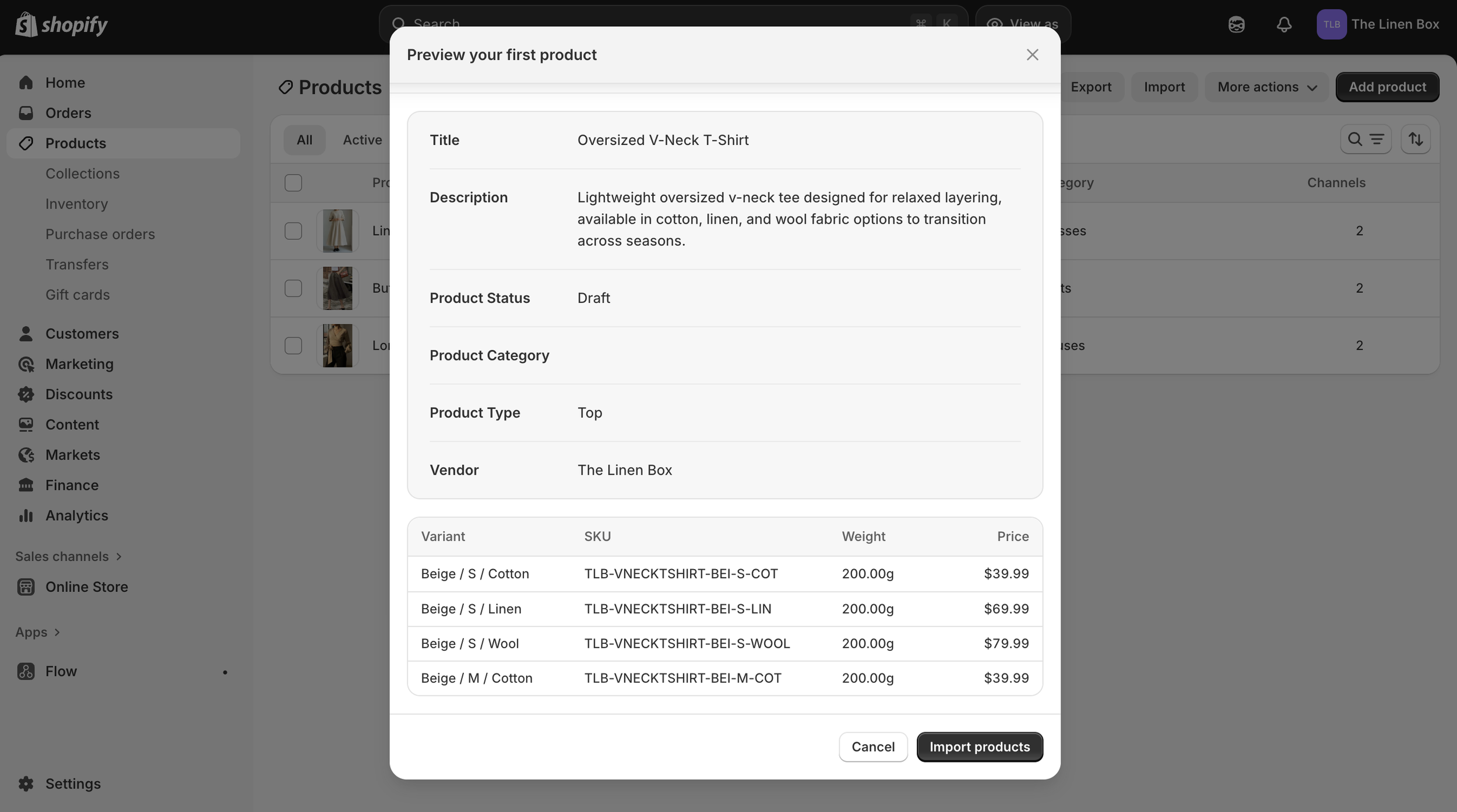
3b. Import Preview
Import preview confirming fields, variants, and price values before publishing.
3c. Draft Admin View After Import
Product created in Draft with images, options, and seeded variant grid from the CSV.
3d. Final Admin View
Completed admin setup with variants, pricing, inventory, category mapping, tags, and SEO metadata.
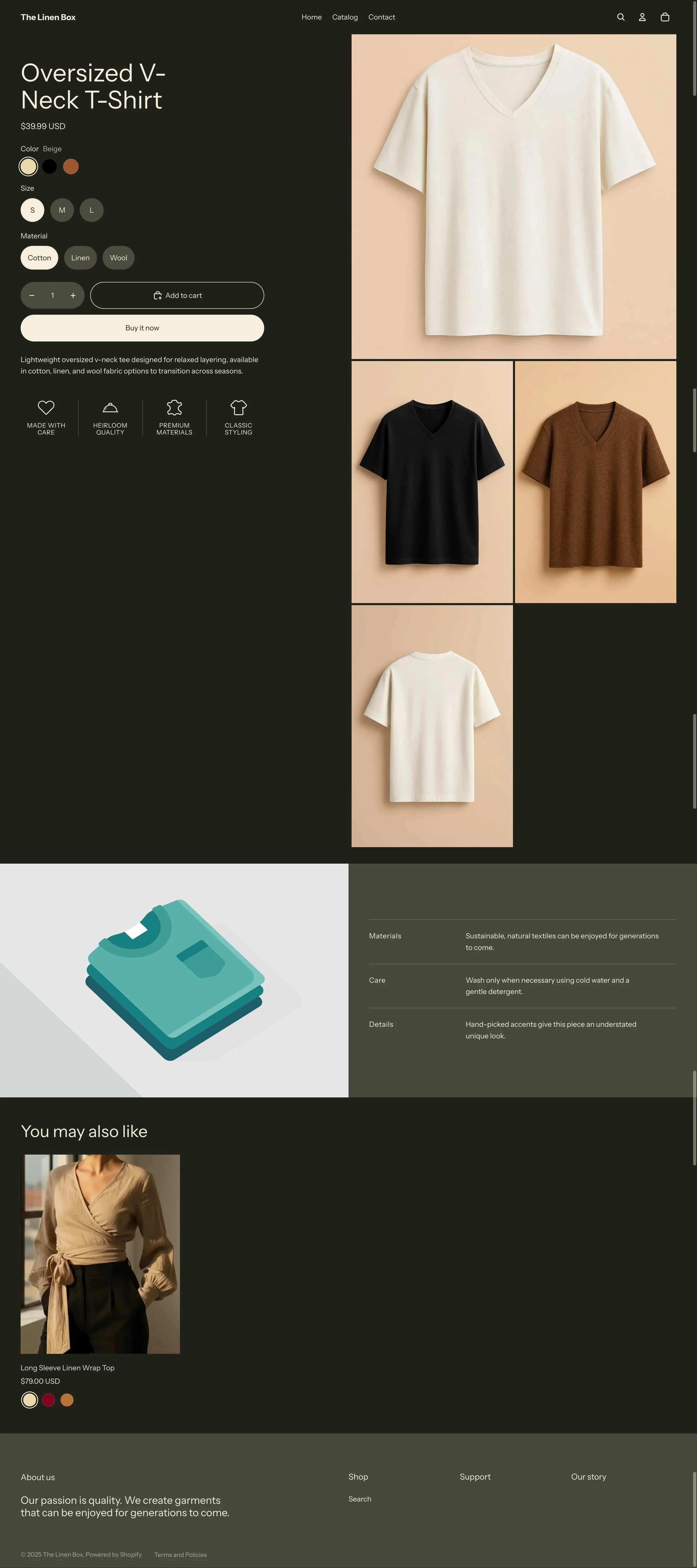
3e. Storefront View
Completed admin setup with variants, pricing, inventory, category mapping, tags, and SEO metadata.
4. Bulk Variant Price Update via CSV Export and Re-Import
Pricing updates often need to be applied across multiple variants at once. While Shopify’s bulk editor can do this, this example demonstrates the scalable CSV method: exporting current variant rows, updating only the price and compare-at fields, and re-importing clean changes. The linen variants were reduced from $69.99 to $64.99 with new compare-at pricing added, keeping SKU integrity and ensuring a controlled, reversible update at scale.
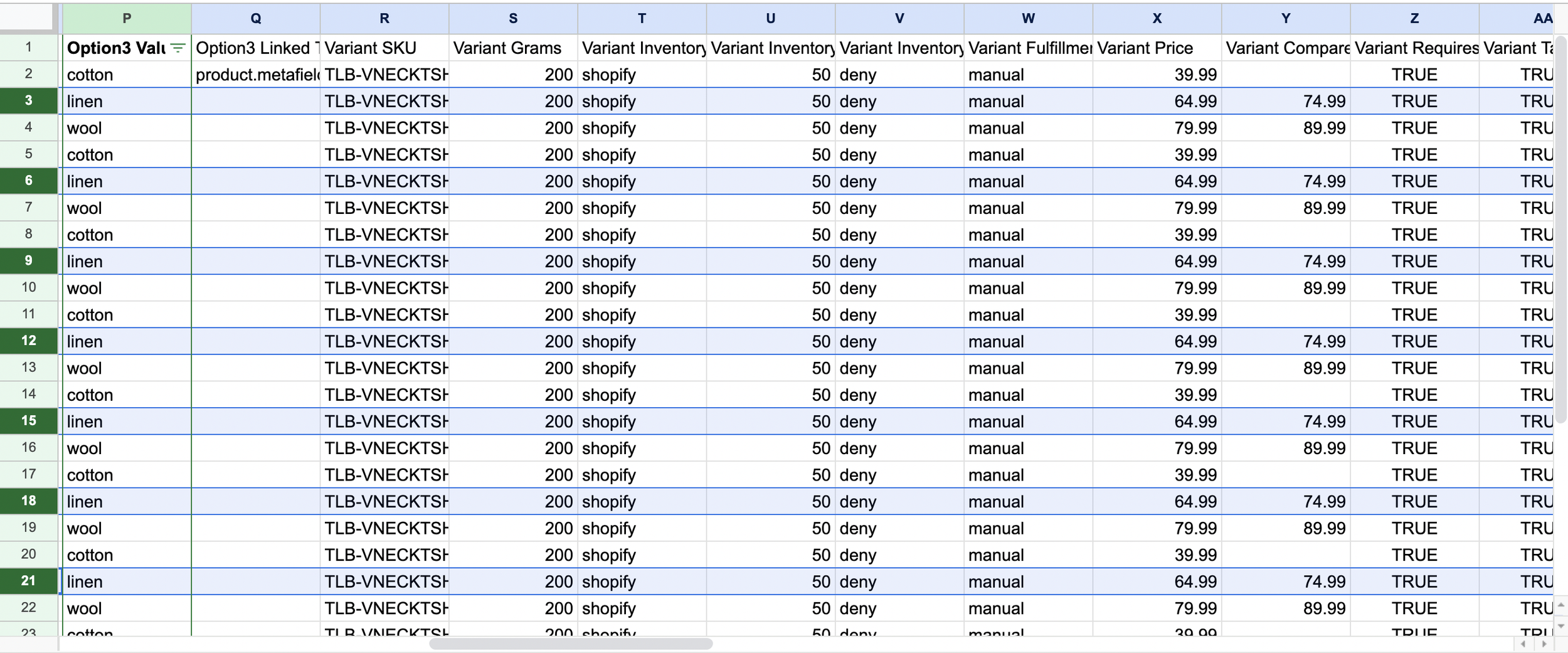
4a. Edited CSV for Price Update
Variant price and compare-at columns updated in the exported file, preserving SKUs, option sets, and inventory columns to avoid overwrites. Prepared for clean import.
4b. Storefront Before Page
Product page before update, showing original price.
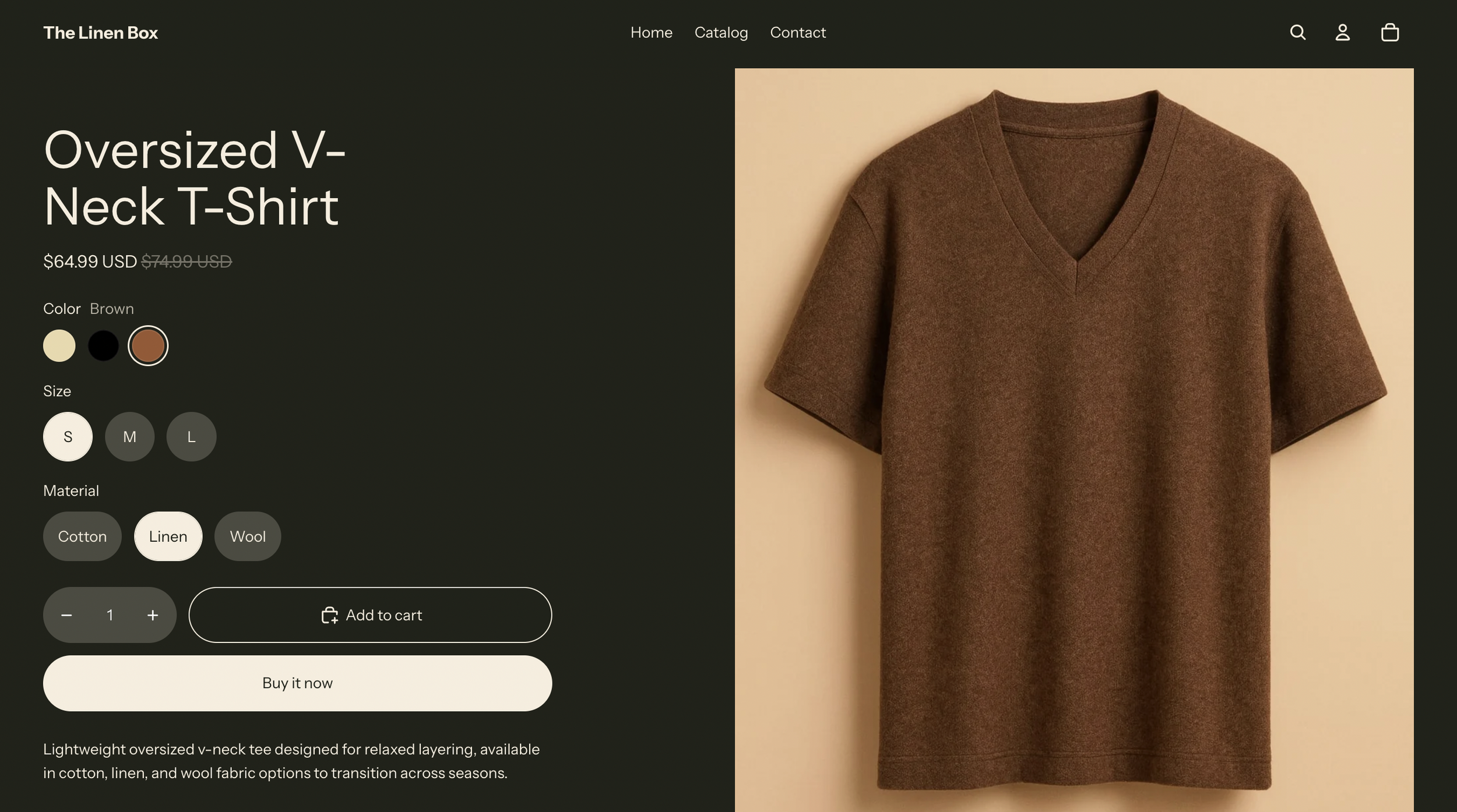
4c. Storefront After View
Storefront after import shows promotional pricing and strike-through compare-at value. On-brand and consistent.
4d. Audit Check
Spot-check confirming compare-at value populated correctly across linen variants only.
5. Bulk Inventory Update via CSV Export and Re-Import
This section updates inventory in bulk by exporting live variant stock levels, adjusting the “On hand (new)” field in an exported inventory CSV, and re-importing clean data. It shows operational control over stock accuracy without manual editing in the admin — a scalable, auditable method for managing multi-variant products and seasonal replenishment.
5a. Admin View — Inventory Before Update
Inventory view before update. Selected variants show “On hand = 50” across sizes and materials.
5b. CSV File — Inventory Update
Exported inventory template edited in the On hand (new) column to 120. SKUs and handles preserved to avoid mismatches.
5c. Admin View — Inventory After Update
Inventory after import. Linen fabric variants now show On hand = 120, confirming a clean update.
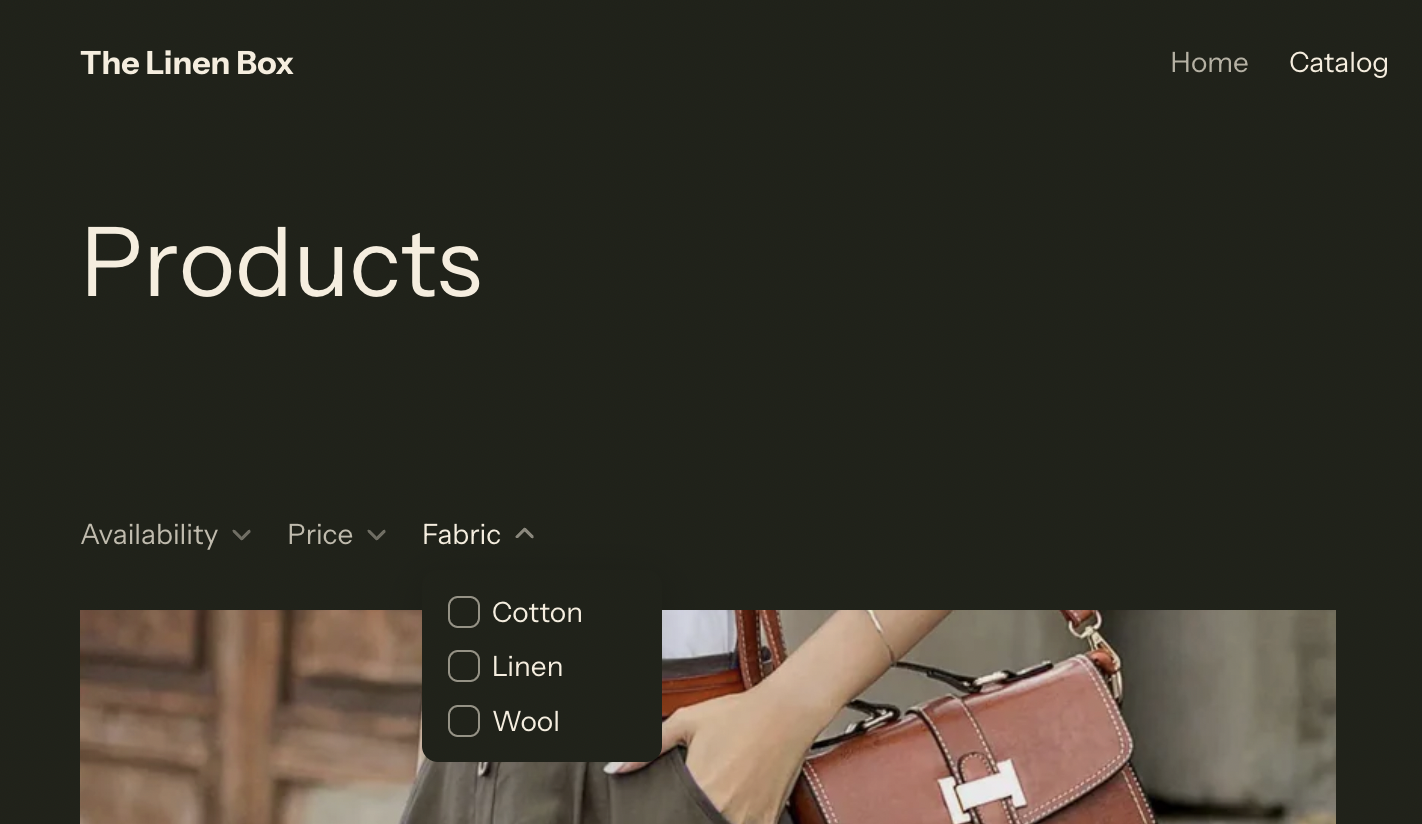
6. Site Filters & Product Recommendations (Search & Discovery)
To support product discovery and outfit-building, I configured Shopify’s Search & Discovery app. I connected the Fabric metafield to storefront filters, confirmed each value, and published faceted navigation on the collection page. I also added complementary and related products to strengthen cross-sell paths on the product page. The result is clear material-based filtering and automated product recommendations that reinforce merchandising and scale as the catalog expands.
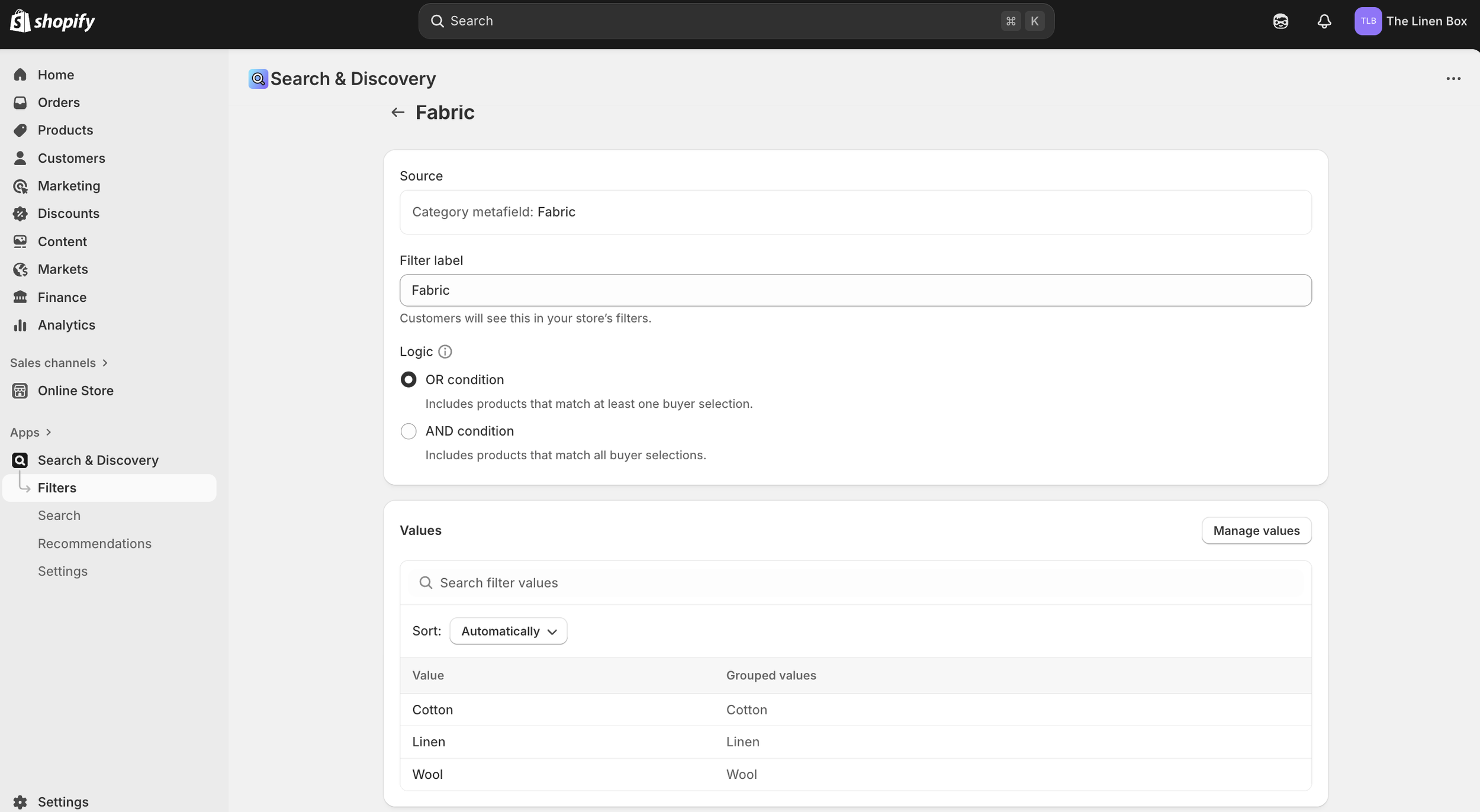
6a. Admin View — Filter Setup
Filter built from the “Fabric” metafield. Cotton, Linen, and Wool surfaced as selectable values with OR logic for inclusive browsing.
6b. Frontend Filter Display
Shopper-facing Fabric filter active on the catalog page, enabling quick material-based narrowing.
5c. Admin View — Product Recommendations
Recommendation rules configured for the Oversized V-Neck: skirt shown as complementary; tops and dresses mapped as related items.
5d. Frontend PDP Product Recommendations
Recommendations displayed live on PDP. Matching garments surfaced to drive attach rate and outfit-building behavior.
Conclusion
This work shows full control over a Shopify catalog from raw data to live merchandising. Products were structured in spreadsheets, imported cleanly, enriched with metadata, and verified in the admin and storefront. Bulk price and inventory updates were executed through exports and controlled CSV edits. Automation flows handled low-stock and restock tagging without manual intervention. Filters and recommendations were configured to support product discovery and cross-sell behavior. The result is a clean, scalable catalog setup with reliable automation, efficient merch workflows, and a polished storefront experience built on accurate data.